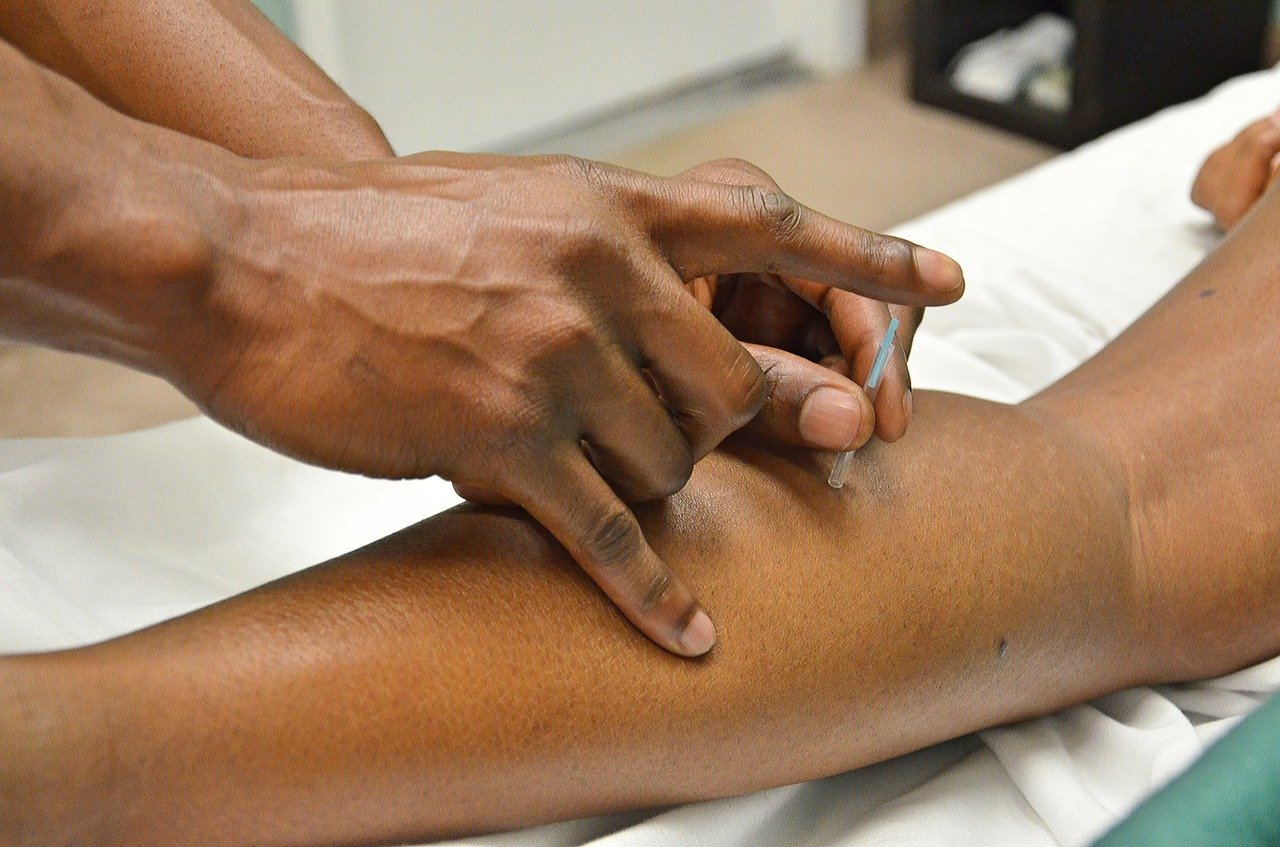
What is dry needling?
Dry needling is an intervention used by many physiotherapists that is similar to acupuncture. It is based on scientific research and uses western-based anatomy and physiology to select trigger points.
What are trigger points?
A trigger point is a tender taught band in a muscle which causes generalised musculoskeletal pain when overstimulated. These are the points that are targeted in dry needling.
What conditions can dry needling be beneficial for?
Physios often use this treatment technique for a range of chronic injuries and conditions including:
- Headache management
- Osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal pain
- Muscle spasms
- Sciatica
- Lateral elbow pain (tennis elbow)
- Neck pain
- Knee pain
- Back pain
How does dry needling work?
Dry needling uses a thin needle to penetrate the skin to stimulate and inactivate underlying trigger points, such as muscular and connective tissues, to reduce your muscle pain and improve your movement.
When would physios consider dry needling?
- To treat dysfunctions in skeletal muscle, fascia, and connective tissue
- To diminish persistent peripheral pain
- To reduce or restore impairments of body structure and function leading to improved activity and participation
What else do you need to know about dry needling?
Practitioners who perform dry needling have completed rigorous training to ensure the treatment is highly effective and meets national safety standards. Dry needling is not a standalone treatment and is often combined with other physio treatments including soft tissue mobilisation and therapeutic exercise. It is recommended you follow the advice of your health professional as to whether dry needling is right for you and your health considerations.
Is a referral required?
No referral is required to see a physio for dry needling.
Can I claim this service as an extra on my health insurance policy?
A dry needling session may be claimed on private health insurance depending on your level of cover, please check with your private health insurance provider.