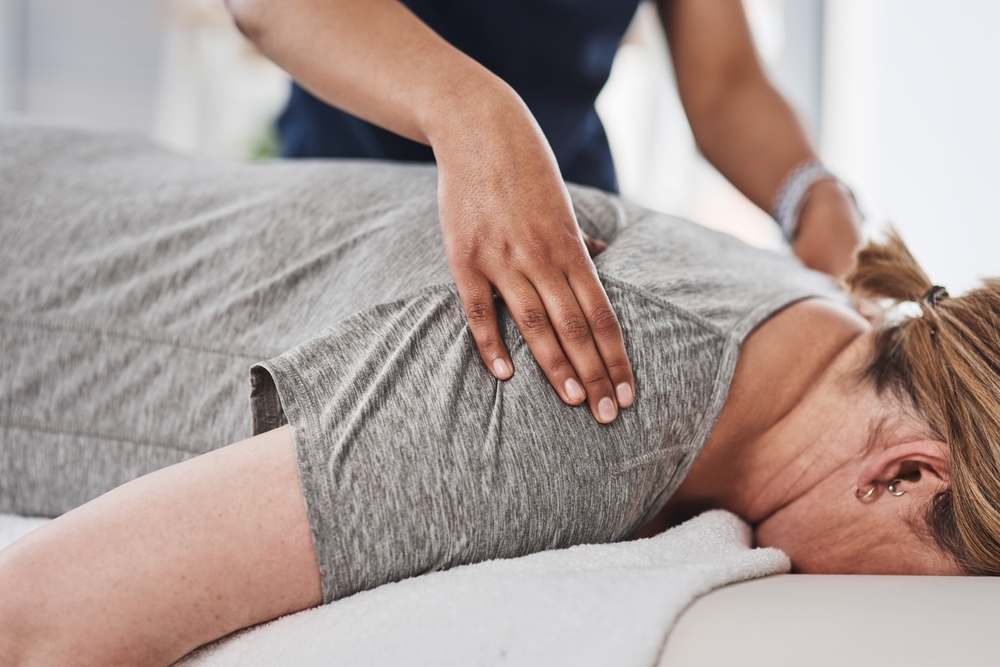
If you’re struggling with persistent pain, tight muscles, or restricted movement, you may have come across the term Myotherapy—but what is Myotherapy exactly? Clinical Myotherapy is a specialised form of treatment designed to relieve musculoskeletal pain, restore movement, and prevent further injury. Unlike general massage, it goes beyond relaxation, using targeted manual techniques, exercise therapy, and education to address the underlying causes of pain and dysfunction.
In this blog, we’ll explore how it works, the conditions it treats, and why it’s an effective solution for long-term musculoskeletal health.
What is Myotherapy? Understanding its foundations
Clinical Myotherapy is a hands-on, evidence-based therapy designed to assess, treat, and rehabilitate musculoskeletal conditions. It targets issues such as muscle tension, joint stiffness, and movement dysfunction using a combination of manual techniques and rehabilitative exercises. Unlike treatments that only address symptoms, Myotherapy focuses on identifying and treating the root cause of pain, providing a structured and personalised approach to pain relief and injury prevention.
To fully understand what is Myotherapy, it’s essential to explore its foundations in musculoskeletal anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics. Clinical Myotherapists undergo extensive training to assess and manage a wide range of conditions, including back and neck pain, sports injuries, and postural imbalances. By restoring movement, improving muscle function, and addressing underlying imbalances, Myotherapy helps individuals move more freely, reduce discomfort, and enhance overall quality of life.
Core principles of Clinical Myotherapy
- Assessment: Clinical Myotherapists conduct comprehensive assessments to identify the underlying causes of pain and dysfunction. This includes evaluating posture, movement patterns, muscle imbalances, and areas of tenderness or restriction.
- Treatment techniques: Clinical Myotherapy integrates various evidence-based manual therapy techniques, including:
- Massage: Various massage techniques used to relax muscles, improve circulation, and alleviate muscular tension.
- Trigger point therapy: Identifies and deactivates trigger points, which are localised areas of muscle spasm or tightness that can refer pain to other parts of the body.
- Dry needling: Similar to acupuncture, dry needling targets trigger points with thin needles to stimulate healing and reduce pain.
- Joint mobilisation: Gentle movements applied to joints to restore range of motion and decrease stiffness.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: Prescribed exercises to enhance flexibility, strength, and function of muscles and joints.
- Rehabilitation: Clinical Myotherapy emphasises rehabilitation to restore function and prevent future injuries. This includes prescribing specific exercises and stretches to address weaknesses or imbalances identified during assessment.
- Education and self-management: Patient education is integral to Clinical Myotherapy, empowering individuals to understand their condition, adopt healthy lifestyle habits, and manage symptoms independently between sessions.
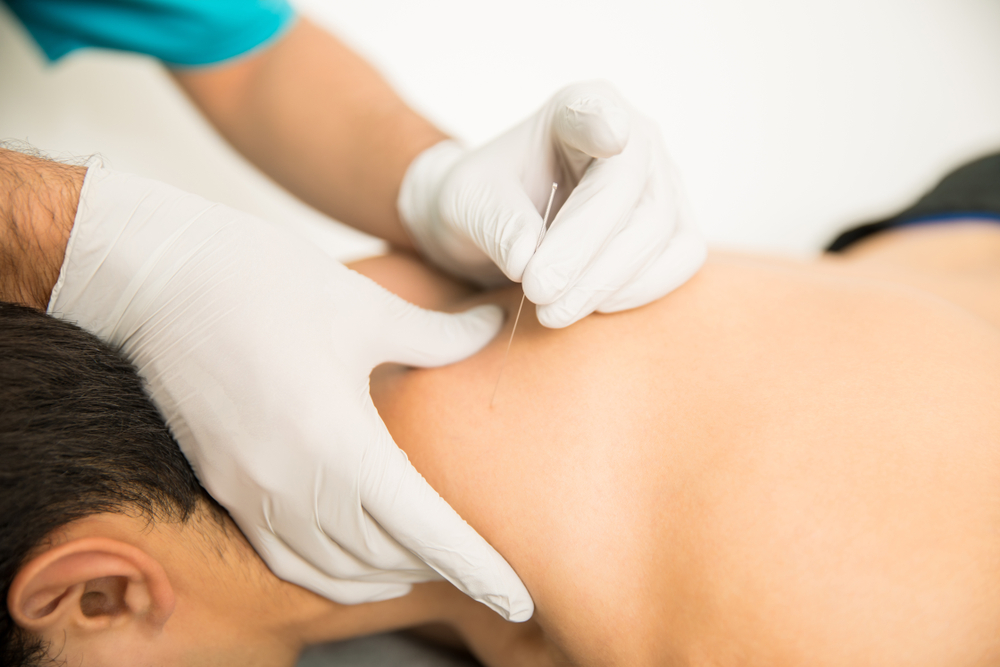
Research evidence supporting Clinical Myotherapy
Research has provided substantial evidence that supports the effectiveness of Clinical Myotherapy across various musculoskeletal conditions and patient populations. Here’s an exploration of the research findings:
Musculoskeletal conditions
Clinical Myotherapy has been shown to be highly effective in managing both acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain. Research findings include:
- Chronic neck and back pain: Studies have shown that Clinical Myotherapy techniques, including trigger point therapy and massage, significantly reduce pain intensity and improve functional outcomes in patients with chronic neck and back pain. For instance, a study published in the Australian Journal of General Practice highlighted the benefits of manual therapy in reducing pain and improving function in patients with non-radicular low back pain.
- Soft tissue injuries: Clinical Myotherapy techniques are effective in treating soft ƒtissue injuries, such as strains and sprains. Research highlights the role of Clinical Myotherapy in speeding up recovery and promoting tissue healing. A systematic review in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy emphasised the effectiveness of manual therapy and exercise in managing acute and chronic low back pain.
- Sports injuries: Athletes benefit from Clinical Myotherapy in rehabilitation and injury prevention. It helps in reducing pain, improving flexibility, and enhancing performance outcomes. Research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy supports the use of soft tissue massage and exercise for treating non-specific shoulder pain.
Chronic pain management
Chronic pain conditions, including fibromyalgia and arthritis, can be significant challenges to patients and healthcare providers. Clinical Myotherapy offers a non-invasive approach to pain management, often reducing reliance on medications and invasive procedures. Research supports its effectiveness in:
- Fibromyalgia: Clinical Myotherapy interventions have been shown to alleviate pain, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall well-being in patients with fibromyalgia. A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy demonstrated the benefits of manual therapy in managing fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Osteoarthritis: Manual therapies, including Clinical Myotherapy, are recommended as adjunct treatments to manage pain and improve joint function in osteoarthritis patients. Research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy highlighted the effectiveness of manual therapy combined with exercise in improving pain and function in knee osteoarthritis.
Functional improvement and quality of life
Beyond pain relief, Clinical Myotherapy focuses on restoring functional abilities and enhancing quality of life. Research outcomes include:
- Mobility and range of motion: Clinical Myotherapy techniques, such as joint mobilisation and therapeutic exercise, contribute to improved mobility and range of motion in patients recovering from injuries or surgery. Studies have shown that these techniques can significantly enhance functional outcomes and reduce recovery time.
- Psychosocial benefits: Patients report psychological benefits, including reduced stress levels and improved mood, following Clinical Myotherapy sessions. These holistic outcomes contribute to overall well-being and patient satisfaction. Research indicates that manual therapy can positively impact mental health by reducing anxiety and depression associated with chronic pain.
Evidence-based practice in Clinical Myotherapy
Clinical Myotherapy practitioners adhere to evidence-based practice guidelines, integrating current research findings into clinical decision-making. This approach ensures that treatment protocols are scientifically grounded and optimised for each patient’s unique needs.
- Clinical guidelines: Organisations such as the Australian Association of Massage Therapists (AAMT) provide clinical guidelines for Clinical Myotherapy practice, emphasising the importance of evidence-based assessment, treatment strategies, and ongoing professional development.
- Research collaboration: Clinical Myotherapists collaborate with healthcare providers and researchers to advance the field through clinical trials, outcome studies, and systematic reviews. This collaborative effort enhances the credibility and efficacy of Clinical Myotherapy as a therapeutic modality.

Integrative healthcare approach
Clinical Myotherapy is increasingly recognised as an integral component of integrative healthcare, complementing conventional medical treatments and promoting multidisciplinary collaboration.
- Patient-centred care: Clinical Myotherapists adopt a patient-centred approach, fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making with patients and other healthcare providers. This approach ensures that treatment plans are tailored to the individual needs and preferences of each patient.
- Complementary therapies: Integrative healthcare settings often incorporate Clinical Myotherapy alongside other modalities such as physiotherapy and acupuncture to provide comprehensive treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. This multidisciplinary approach enhances treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Is Myotherapy Right for You? Take the Next Step in Your Recovery
Clinical Myotherapy is a valuable therapeutic option for individuals seeking relief from musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction. With a strong foundation in research and clinical expertise, it continues to evolve as an effective and evidence-based practice. By integrating advanced assessment techniques, personalised treatment plans, and patient education, Clinical Myotherapy plays a crucial role in improving movement, reducing pain, and enhancing quality of life.
Book an appointment with Lifecare today to discover how Clinical Myotherapy can support your recovery and overall well-being.
Written by Jason Quigley, Clinical Myotherapist – Backfocus Physiotherapy
With a long history at elite national and international sport and a clinical approach to manual therapy, Jason applies a clinical reasoning and manual approach to aiding patients getting back to the best versions of themselves.
References
Adam Parr, Geoffrey Askin, Non-radicular low back pain: Assessment and evidence-based treatment, Australian Journal of General Practice, Volume 49, Issue 11, November 2020.
Alexander Tsertsvadze et al., Cost-Effectiveness of Manual Therapy for the Management of Musculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials, Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, 2014.
Australian Association of Massage Therapists (AAMT), Clinical Guidelines for Myotherapy Practice. Integrative healthcare settings and multidisciplinary collaboration in Clinical Myotherapy.
Easthope, G., Tranter, B. and Gill, G., General practitioners’ attitudes toward complementary therapies, Social Science & Medicine, 2000.
Nils Runge et al., The Benefits of Adding Manual Therapy to Exercise Therapy for Improving Pain and Function in Patients with Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis, Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 2022.
Paul Andrew van den Dolder et al., Effectiveness of soft tissue massage and exercise for the treatment of non-specific shoulder pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis.
Shahnawaz Anwer et al., Effects of orthopaedic manual therapy in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis 2018.
Steven Z. George et al., Interventions for the Management of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain: Revision 2021, Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy 2021 51:11, CPG1-CPG60.